How California Wildfires Impact Supply Chain
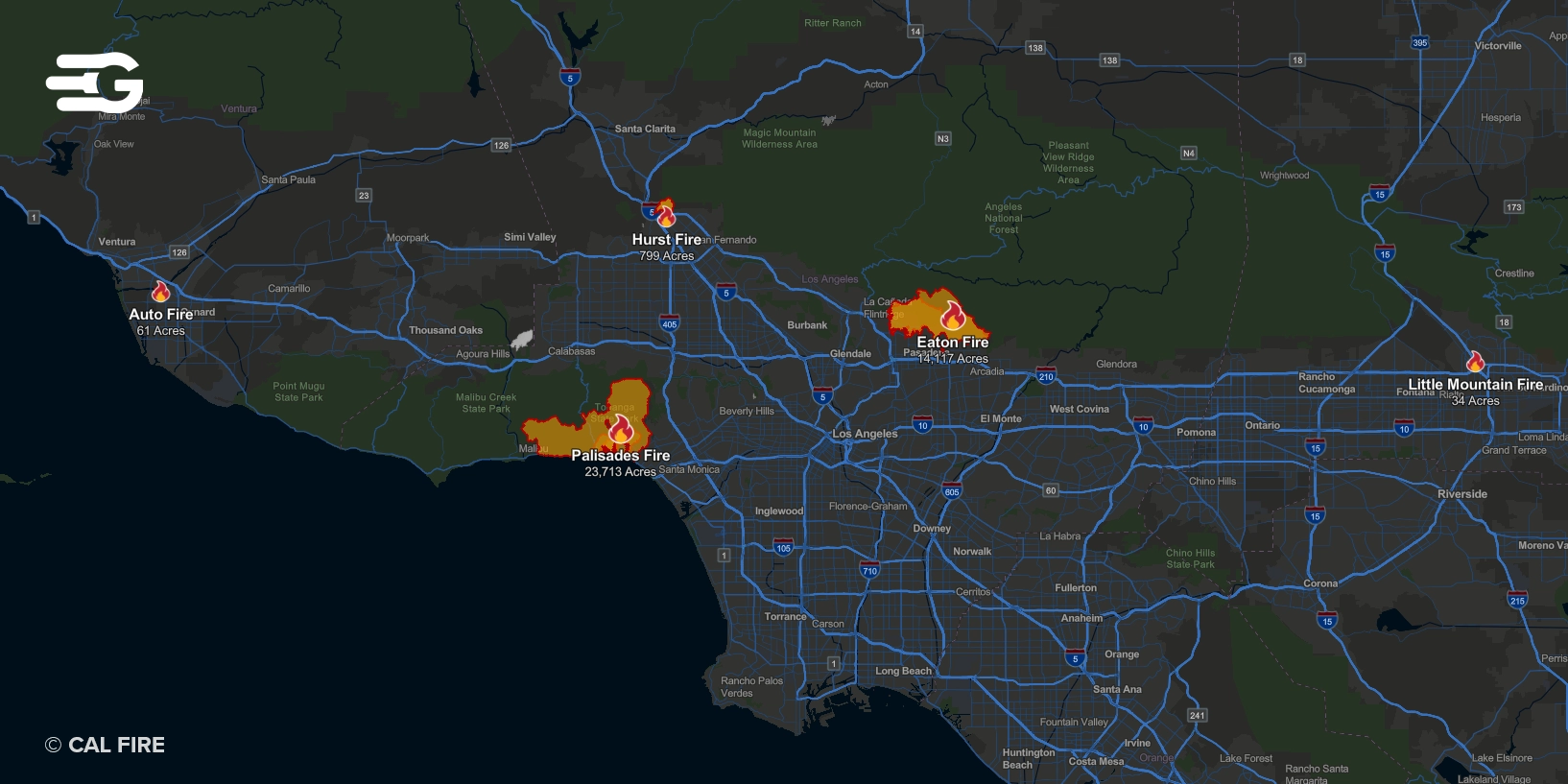
Over the last two weeks California has been in an ongoing battle with wildfires, particularly in the Los Angeles area. The Santa Ana winds, combined with dry conditions have on-set one of the biggest fires in history. With an estimated damage of 40,000 acres, Palisades, Malibu, Altadena, Pasadena, Sylmar and Eaton are the worst affected by the crisis.
California is a critical international hub, home to the Port of Los Angeles and Long Beach. As quintessential stops for the global economy, developments in this region have far-reaching effects on supply chains worldwide. As flames engulf vast areas, road closures, limited storage capacities, and logistical bottlenecks are straining the movement of goods and services.
Supply chains for essential goods, including food and medical supplies, are under immense pressure, as many warehouses and distribution centers in affected areas either shut down or operate at reduced capacity. The situation is particularly dire for perishable goods, which face a heightened risk of spoilage due to transportation delays and limited cold storage availability.
While nearby ports remain operational, the ongoing disruptions highlight the vulnerability of supply chain infrastructure and on-road transportation.
Impact on Road Transport
The California wildfires have significantly disrupted trucking operations and the broader supply chain in the region. The California Trucking Association CEO, Eric Sauer, told Trucking Drive, an online publication, that the Santa Ana winds were causing hurdles before the fires started, such as potential truck rollovers.
Over the past two weeks, multiple road closures and mass evacuation have affected freight movement.
Highway Closures and Traffic Congestion: Major highways, including parts of the Pacific Coast Highway and Interstate 405, have been closed due to fire activity and smoke, cutting off critical transport routes. Additionally, mass evacuations of around 110,000 residents have led to severe traffic congestion, particularly on major routes like Interstate 5.
Increased Delays and Costs: Freight and delivery companies have reported significant delays, with rerouted trucks facing longer transit times and increased fuel costs.
Air Quality and Visibility Issues: Smoke from the wildfires has reached areas like San Pedro Bay, causing air quality and visibility problems that complicate trucking operations.
Port Congestion
Ports in the Los Angeles area remain operational but are facing severe congestion. With limited resources available for cargo movement due to the California wildfires, delays in unloading and transportation are leading to longer container dwell times at docks.
This is resulting in significant demurrage fees, as containers remain in port past the allotted free time. As congestion continues to build, businesses may face escalating costs, impacting the efficiency of supply chains and increasing financial strain.
Limited dockworker availability and disruptions in road infrastructure are further exacerbating the situation, causing a backlog of cargo that could further extend delays and raise operational costs for shippers and importers.
Air Cargo Movement
There has also been a significant impact on air travel and cargo handling. At Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), approximately 500 flight delays and 13 cancellations occurred over a recent weekend due to poor visibility from smoke.
Hollywood Burbank Airport also saw 41 out of 70 scheduled flights canceled because of strong winds. These delays are hindering air cargo operations, creating extended waiting times for unloading and limited transport options.
Air cargo delays are further compounded by the lack of available ground transportation, making it harder to move goods efficiently.
2021 British Columbia Fires Impact on Supply Chains
The 2021 wildfire in British Columbia caused similar disruptions on global supply chains. Though the expanse and projected impact of the California wildfires is higher, hindsight can prove to be crucial in a time like this.
Transportation Disruptions:
- Rail and Road Closures: Wildfires in south-central BC disrupted major rail lines and highways, significantly delaying the movement of goods across the province and beyond. These interruptions exposed critical weaknesses in transportation networks, particularly for retail and essential goods distribution.
- Port of Vancouver: As Canada’s largest port, the Port of Vancouver experienced operational challenges due to limited access and rerouted shipments, further exacerbating delays in imports and exports.
Economic Impact:
- Rising Supply Chain Costs: The forest products sector in BC reported substantial expenditures, with supply chain costs growing at a compound annual rate of 10.2% from 2018 to 2022. While figures specific to 2021 were not detailed, the disruptions caused by the wildfires undoubtedly contributed to increased operational costs.
What Can You Do?
In conditions like this, businesses must adopt strategic measures to maintain supply chain stability and minimize delays. Here are key steps you can take to navigate these challenges effectively.
1. Diversify Transportation Routes and Hubs:
Air: Shift some cargo operations to less-affected regional airports like Ontario International Airport or even airports outside the immediate wildfire zone.
Ports: Consider rerouting shipments to other nearby ports, such as the Port of Oakland or San Diego, to reduce congestion and avoid prolonged delays.
2. Increase Visibility Through Technology:
Utilize supply chain visibility tools like GoComet’s GoTrack to monitor real-time delays at ports and airports. These platforms can help businesses proactively adjust their shipping plans based on congestion or weather-related disruptions.
Employ predictive analytics to forecast potential delays and costs, helping optimize resource allocation.
3. Prioritize Critical Freight:
Implement cargo prioritization protocols to ensure essential goods, such as perishable items and medical supplies, are moved first. This can be achieved by working closely with logistics partners to identify priority shipments.
4. Optimize Inventory Management:
Rethink inventory strategies by increasing buffer stocks or storing goods in locations less likely to face wildfire-related disruptions. Use regional distribution centers to position inventory closer to end consumers, reducing reliance on heavily affected areas.
5. Collaborate with Carriers and Forwarders:
Maintain open communication with logistics providers to gain updates on road closures, flight schedules, and port congestion. Negotiate flexible contracts with carriers to minimize costs associated with demurrage or rerouting.
6. Strengthen Crisis Management Protocols:
Develop and test disaster recovery plans for supply chain disruptions, including contingencies for wildfire scenarios. Train teams to respond quickly to unforeseen disruptions, including identifying alternative transportation modes or partners.
7. Leverage Multimodal Transportation:
Use rail or sea freight to supplement trucking operations, particularly for long-haul shipments, to bypass roadblocks and wildfire-affected routes. Explore short-haul alternatives like barges to move goods from congested ports to inland hubs.
Emphasizing Sustainability
The wildfires underscore the urgent need to integrate sustainability into supply chain operations. Adopting eco-friendly practices not only helps mitigate the environmental impact of logistics but also builds resilience against climate-related disruptions. Companies can invest in alternative fuels, energy-efficient transportation, and carbon offset programs to reduce their carbon footprint.
Moreover, integrating sustainable sourcing and adopting circular supply chain practices can minimize dependency on vulnerable regions and create a more robust global network. Long-term planning focused on sustainability ensures that businesses are not only reactive to crises but also proactive in addressing the root causes of disruptions like wildfires.
The California wildfires serve as a wake-up call for the supply chain industry to adapt and evolve. By prioritizing sustainability, leveraging technology, and adopting strategic contingency measures, businesses can navigate current disruptions while building a more resilient and future-ready infrastructure.