Essential To Global Trade Compliance And Regulation
In today’s connected global economy, businesses rely on the smooth movement of goods across borders. However, this requires navigating a complex set of trade regulations and compliance standards. For enterprises managing large shipments with freight forwarders, understanding global trade compliance is crucial to success. Recent estimates highlight that non-compliance can cost businesses billions annually due to penalties, delays, and lost market opportunities.
What is Global Trade Compliance?
Global trade compliance involves adhering to the laws, regulations, and policies that govern the international movement of goods. These include:
- Import/export procedures for ensuring proper documentation and approvals.
- Accurate classification of goods using Harmonized System (HS) codes.
- Determining the country of origin to meet trade agreement standards.
Each country implements unique trade policies, necessitating businesses to stay updated with regional regulations. Failure to comply can result in significant financial losses, shipment delays, or even bans from specific markets. Reports highlight that organizations proactively addressing shifting customs laws can save millions annually in penalties and disruptions.
Robust trade compliance frameworks also mitigate risks by up to 40%, enhancing supply chain reliability and efficiency. For instance, adopting a centralized compliance system allows companies to streamline workflows, improve data accuracy, and ensure adherence to ever-evolving trade laws.
Why Global Trade Compliance Matters
Adhering to trade compliance is not just about avoiding penalties, it’s a key driver of operational and strategic success. Here’s how it directly impacts businesses:
- Legal Operations: Ensures adherence to international laws, minimizing the risk of fines, legal actions, or revocation of trading licenses. Recent analyses highlight that non-compliance fines have risen by 20% over the past decade.
- Supply Chain Stability: Proper compliance reduces shipment delays, prevents disruptions, and ensures smoother customs clearance. Companies that maintain strong compliance protocols report up to a 30% reduction in supply chain bottlenecks.
- Market Access: Following trade rules and agreements enables eligibility for preferential tariffs and facilitates entry into regulated markets. This creates a competitive edge in global trade, allowing businesses to unlock growth opportunities.
- Reputation: Ethical practices and compliance frameworks build stakeholder trust, safeguarding brand credibility. Surveys reveal that organizations with robust compliance measures are more likely to attract long-term partnerships.
A comprehensive review of trade compliance trends found that businesses prioritizing these measures achieve an average 25% increase in global market accessibility compared to non-compliant peers.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Violating trade compliance regulations can have far-reaching consequences for businesses, including:
1. Financial Penalties
Regulatory authorities impose steep fines for non-compliance. Over the past decade, fines have risen by more than 100%, with some businesses facing penalties in the millions for repeat offenses.
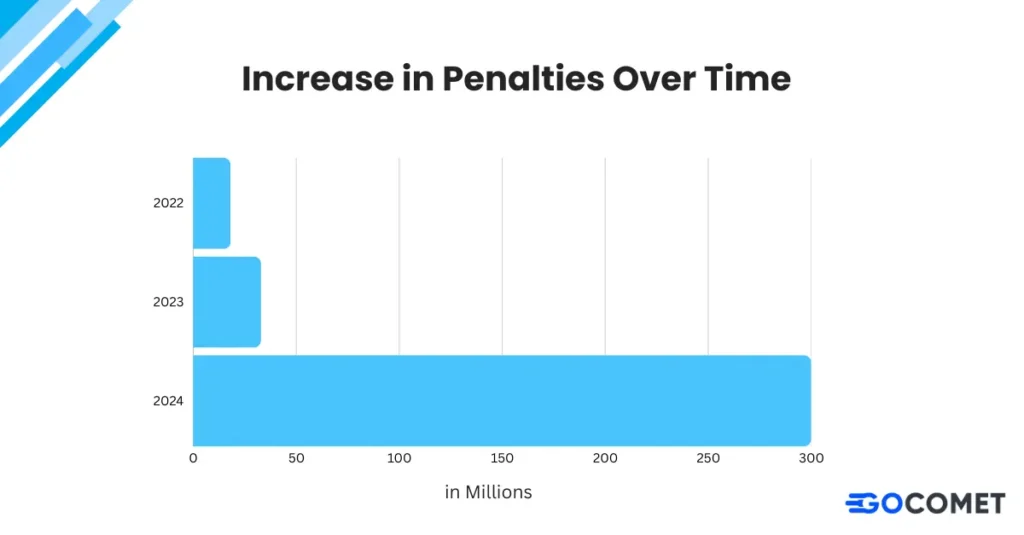
2. Legal Actions
Companies risk trading bans, lawsuits, and revoked licenses, which disrupt operations and create long-term legal challenges.
3. Operational Disruptions
Delays at customs, rejected shipments, or confiscated goods lead to revenue losses and damaged relationships with key customers.
4. Market Restrictions
Non-compliant businesses may be excluded from lucrative international markets, losing access to trade benefits such as preferential tariffs or agreements.
5. Reputation Damage:
Ethical lapses and regulatory violations tarnish corporate reputations, eroding customer trust and investor confidence. Rebuilding trust can take years and require significant investment.
These challenges collectively cost large enterprises millions annually. Beyond financial losses, non-compliance disrupts supply chains. damages brand equity, and threatens long-term viability. Proactive risk management and adherence to global trade standards are essential to mitigating these risks effectively.
Overcoming Compliance Challenges
Businesses encounter multiple hurdles when managing global trade compliance, including:
- Diverse Laws: Each nation enforces distinct and often complex regulations regarding sanctions, customs, and export controls. This variability demands tailored compliance strategies for each market.
- Internal Pressures: Companies face increasing demands to streamline their supply chains, reduce costs, and meet delivery deadlines while maintaining compliance.
- Frequent Regulation Changes: Rapid policy shifts at national and international levels necessitate constant monitoring and swift adaptation.
Advanced technology solutions are transforming compliance management. For example, AI-enabled systems analyze trade rules to ensure precise classifications, thereby reducing tariff costs and preventing errors. Businesses adopting such tools report significant savings, with some reducing classification inaccuracies by over 50%. AI also predicts regulatory changes, enabling companies to stay ahead of compliance challenges and avoid disruptions.
Leveraging Technology for Trade Compliance
Technology can simplify complex compliance tasks. Solutions like AI-driven analytics and blockchain enable:
- Real-time risk monitoring.
- Accurate documentation and record-keeping.
- Enhanced visibility across the supply chain.
AI applications in trade compliance have already helped some businesses achieve 15% faster processing times for cross-border transactions. Blockchain’s ability to provide immutable records ensures transparency, reducing the likelihood of disputes.
Creating a Culture of Compliance
Building a robust compliance culture requires a combination of education, policy enforcement, and leadership commitment. Here are critical steps to establish such a culture:
- Tailored Training Programs: Equip employees with the knowledge to handle compliance challenges specific to their roles. For example, customs teams benefit from focused HS code classification training, while finance teams gain insights into tariff management.
- Clear Policies Against Ethical Violations: Implement strong anti-bribery and corruption policies with clear reporting mechanisms. Encourage a “speak-up” culture where employees feel empowered to report concerns without fear of retaliation.
- Practical Case Studies and Simulations: Use real-world examples to highlight the consequences of non-compliance and teach best practices. Interactive learning tools, such as scenario-based training, enhance understanding and retention.
Investments in continuous compliance education have been shown to reduce violations by 30% or more. Additionally, organizations that foster compliance as a core value see increased employee accountability and operational efficiency.
The Role of Compliance in the Supply Chain
Global trade compliance is an integral aspect of supply chain management, ensuring smooth and ethical operations from procurement to delivery. By adhering to compliance standards, businesses can achieve the following:
- Smooth Operations: Effective compliance prevents customs delays, shipment holds, and other logistical interruptions, enabling on-time deliveries.
- Cost Savings: Avoiding non-compliance penalties and optimizing tariff classifications reduces costs significantly, with some businesses reporting up to 15% savings on total shipment expenses.
- Risk Mitigation: Proper compliance reduces exposure to fraud, illegal activities, and regulatory scrutiny, safeguarding the company’s reputation and financial health.
A study found that integrating compliance measures at every stage of the supply chain can reduce operational risks by up to 50% and enhance overall efficiency. For instance, automating compliance checks during procurement and shipment processes minimizes errors and ensures adherence to international regulations.
Conclusion
For enterprises managing large-scale shipments, global trade compliance is the foundation of ethical and efficient operations. By following regulations, leveraging technology, and fostering a compliance-driven culture, businesses can navigate the complexities of international trade with confidence and ease. Maintaining compliance not only safeguards operations but also unlocks growth opportunities in competitive markets.






