Reverse Logistics: A Comprehensive Guide
Reverse logistics is becoming a crucial area of focus in today’s business environment, where the “customer is king” and delivering a great customer experience is crucial. In an increasingly competitive market, businesses which are unable to effectively manage returns run the danger of losing clients. However, what is reverse logistics precisely, and how does it work with the current supply chain?
What is Reverse Logistics?
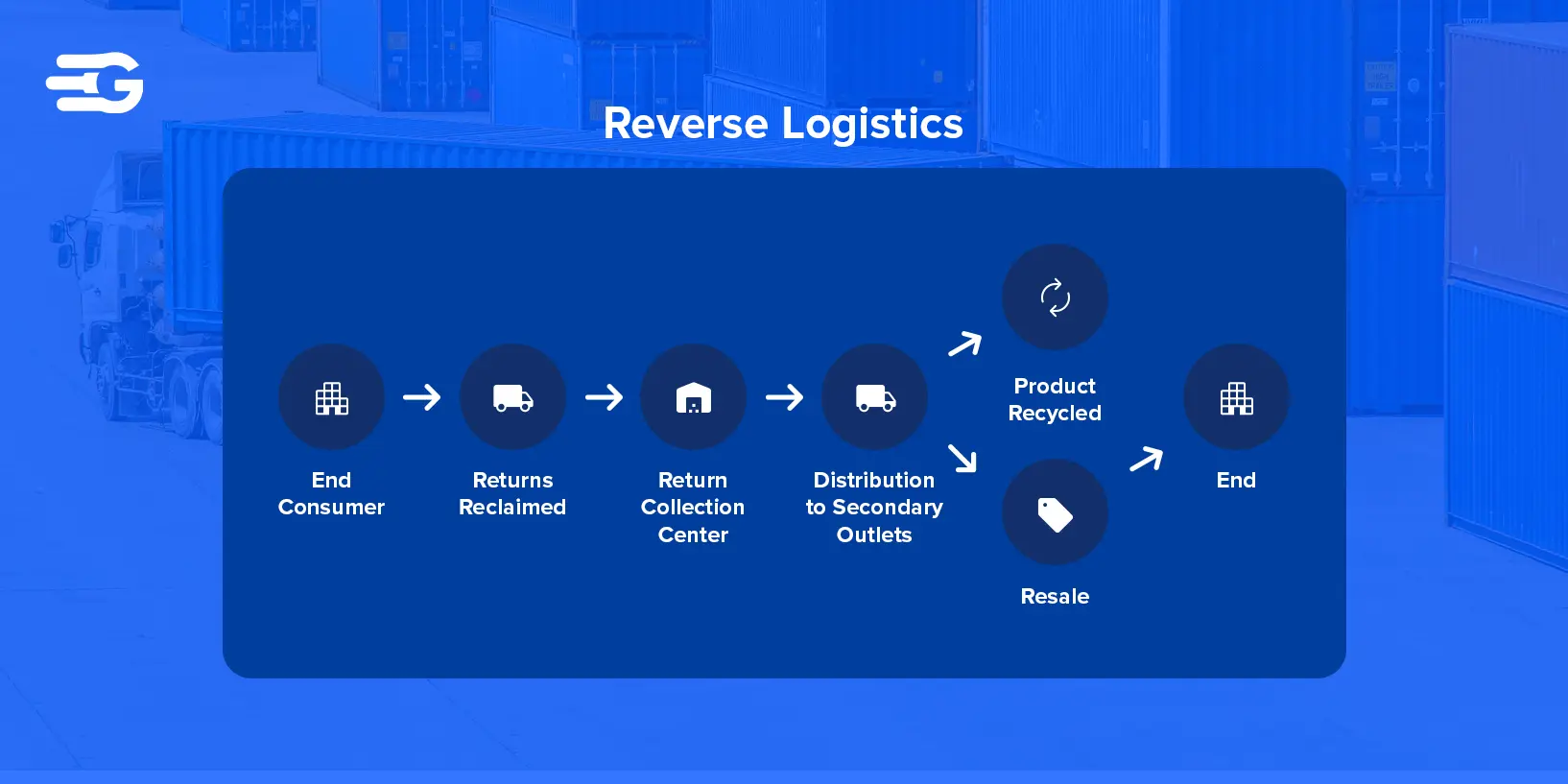
Reverse logistics refers to managing the return flow of goods from the end user back to the origin or designated processing centers. It includes activities like handling returns, refurbishing products, recycling materials, and safely disposing of waste. For businesses handling large volumes of freight, reverse logistics ensures smoother operations and cost optimization.
This process is essential for recovering value from returned items and minimizing waste. For instance, defective goods can be returned for repair or resale, while recyclable materials can be reprocessed to reduce environmental impact. By integrating return logistics into the supply chain, businesses can enhance profitability, improve customer satisfaction, and support sustainability goals.
For a deeper understanding of the broader logistics management practices, you might explore what is transport and logistics management.
Types of Reverse Logistics
End-of-life product logistics involves several key processes, each essential for managing the backward flow of goods efficiently.
- Returns Management: This process involves accepting and processing customer returns, whether for refunds, replacements, or repairs. It directly impacts customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- Recycling Programs: These focus on collecting and processing used materials like packaging, electronics, or plastics for reuse. Effective recycling programs help reduce raw material costs and environmental impact.
- Repair and Refurbishment: Products with minor defects or wear are repaired or refurbished to a sellable condition. This reduces waste and creates opportunities to recapture value.
- Product Recalls: Ensuring the safe and organized return of faulty or unsafe products protects customer safety and brand reputation. A clear recall strategy minimizes disruptions.
- End-of-Life Disposal: Items that can no longer be used or repaired are responsibly disposed of, often through recycling or certified waste management services.
Each type is tailored to address specific challenges within the supply chain, contributing to cost savings, sustainability, and customer trust.
5Rs of Reverse Logistics
The 5Rs form a strategic approach to managing reverse logistics effectively. Each element contributes to sustainability and operational efficiency.
- Returns: Create seamless and customer-friendly return policies. Digital tools like return portals improve speed and transparency, enhancing trust.
- Repair: Establish in-house repair systems or partner with specialists. Repairing goods extends their lifespan and reduces the need for replacements, saving costs.
- Reuse: Promote reusable packaging and materials across the supply chain. This minimizes waste and lowers recurring procurement expenses.
- Recycle: Implement robust recycling programs. Processing returned items like electronics or packaging into raw materials reduces environmental impact and dependence on virgin resources.
- Resell: Identify opportunities to refurbish and resell returned goods. Outlet stores and online marketplaces offer profitable avenues for selling like-new items.
By embedding these practices into their operations, businesses can achieve lower costs, enhanced customer loyalty, and a stronger commitment to sustainability.
Importance of Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management
Reverse logistics is essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive and sustainable. It enables the efficient handling of returns, minimizes waste, and ensures value recovery from used or defective products. End-of-life product logistics also intersects with broader logistics practices, as detailed in supply chain vs logistics management.
For freight-intensive industries, after-sales logistics offers significant advantages. Consolidating return shipments reduces transportation costs and improves operational efficiency. Recycling programs help enterprises lower their environmental footprint by diverting materials from landfills and reintroducing them into production cycles. These measures not only enhance profitability but also strengthen customer trust and long-term business relationships.
Furthermore, end-of-life product logistics ensures compliance with environmental regulations, which is critical in industries like electronics and manufacturing. By aligning operations with sustainability goals, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for eco-friendly practices.
Benefits of Optimized Reverse Logistics
Optimizing return logistics delivers clear advantages that benefit businesses, customers, and the environment:
- Cost Savings: Reusing components and refurbishing products reduce manufacturing expenses. Consolidating return shipments minimizes freight costs and optimizes route efficiency.
- Customer Retention: A hassle-free and transparent return process improves customer satisfaction and loyalty, encouraging repeat business.
- Environmental Impact: Recycling materials and refurbishing goods significantly reduce landfill waste and the need for virgin resources, supporting sustainability efforts.
- Inventory Management: By analyzing return data, businesses can maintain balanced stock levels, avoiding excess inventory or stockouts, which directly affects profitability.
These benefits not only improve operational efficiency but also enhance brand reputation, enabling businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers and stakeholders.
Reverse Logistics vs. Traditional Logistics
Traditional logistics focuses on delivering goods to customers, emphasizing efficient distribution and timely delivery. Reverse logistics, on the other hand, manages the flow of goods back to the origin, handling returns, repairs, recycling, and disposal.
Both play crucial roles in maintaining a seamless supply chain. For instance, traditional logistics ensures that products reach customers in excellent condition, while after-sales logistics deals with items sent back due to defects, customer returns, or end-of-life processing. Together, they support a closed-loop system, improving cost efficiency and sustainability for businesses handling large volumes of shipments.
Reverse Logistics vs. Reverse Supply Chain
Reverse logistics focuses on specific operational activities like processing returns, repairs, recycling, and refurbishment. It deals with the direct movement of goods back through the supply chain. Conversely, the reverse supply chain encompasses a broader scope, including all steps from collection to redistribution, ensuring a complete loop.
Integration of both is vital for achieving a circular economy. This requires tracking returned goods, assessing their condition, and efficiently reintroducing them into the production cycle.
Such coordination improves resource utilization, minimizes waste, and supports sustainable supply chain practices, ultimately creating value for businesses and their stakeholders.
Strategies for Reverse Logistics Improvement
Enhancing reverse logistics requires strategic and well-planned actions. These measures not only boost efficiency but also contribute to long-term sustainability. Businesses can also benefit from understanding logistics route optimization to enhance the reverse flow of goods.
- Use Advanced Technology: Adopt systems like RFID, GPS, and IoT-enabled trackers to monitor returns in real-time. These technologies provide transparency, reduce delays, and improve accuracy in handling goods.
- Streamline Returns: Develop customer-friendly return policies and automated return portals. This simplifies the process, reduces time, and enhances the overall customer experience.
- Leverage Data Analytics: Use advanced analytics tools to study return patterns and identify trends. Insights gained can inform better inventory planning, reduce future returns, and optimize logistics operations.
- Collaborate with Logistics Experts: Partner with specialized logistics providers and freight forwarders. They bring expertise and infrastructure to efficiently manage large volumes of returns and recycling processes.
- Implement Sustainable Practices: Prioritize the use of recyclable packaging and refurbished goods. Encourage circular practices like refurbishing, remanufacturing, and responsible disposal to align with environmental goals.
By adopting these strategies, businesses can optimize reverse logistics and improve performance across their supply chains.
Real-World Examples of Reverse Logistics
Patagonia, the outdoor clothing company, exemplifies the power of reverse logistics in fostering sustainability. Their Worn Wear program addresses the growing issue of textile waste by encouraging customers to repair and extend the life of their Patagonia gear.
For items that cannot be repaired, Patagonia offers a trade-in system where customers receive store credit for used gear. These items are then resold at discounted rates, extending their lifecycle and making sustainable options accessible to more consumers. Through partnerships with textile recycling facilities, Patagonia ensures that unusable garments are processed into new fibers, reducing dependency on virgin materials.
A noteworthy collaboration with Eastman resulted in recycling 8,000 pounds of discarded clothing using molecular recycling technology. This innovative approach showcases the potential of return logistics in minimizing waste and conserving resources.
The Worn Wear program has significantly enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty by aligning with environmental values. Financially, it benefits the business by reducing raw material costs and creating new revenue streams through resales. Patagonia’s efforts underline the transformative impact of return logistics on both sustainability and profitability.
The Future of Reverse Logistics
The future of reverse logistics is promising, with technology playing a central role in its evolution. Advancements in automation and data-driven decision-making are set to revolutionize the field.
Artificial intelligence (AI) will likely become a key tool, helping businesses forecast return volumes, streamline sorting, and provide customers with personalized return experiences. Additionally, robotics will simplify processes like product disassembly and recycling, boosting productivity while reducing labor costs.
A major focus will be on establishing a circular economy, where goods are designed for easy disassembly and reuse. This shift will require closer collaboration between manufacturers and retailers to create products with their end-of-life in mind.
As businesses adopt these practices, after-sales logistics will contribute significantly to reducing waste and mitigating environmental impacts. Intelligence, efficiency, and sustainability will define the future of reverse logistics, shaping it into a vital component of modern supply chains.
Conclusion
Reverse logistics is vital for businesses handling large-scale shipments. It delivers measurable advantages such as significant cost savings through streamlined returns and repairs, improved customer satisfaction due to efficient return processes, and enhanced sustainability by reducing waste and reintroducing materials into the production cycle.
Companies can build a resilient supply chain that fosters long-term profitability and environmental responsibility by implementing advanced reverse logistics practices.
FAQs
What industries benefit from reverse logistics?
Industries such as retail, manufacturing, e-commerce, and electronics significantly benefit from reverse logistics. These sectors deal with high volumes of returns, making efficient reverse processes critical to cost savings and customer satisfaction.
How does reverse logistics support sustainability?
Reverse logistics reduces waste by enabling recycling, reusing, and refurbishing of materials and products. It minimizes landfill contributions and supports circular economy practices by reintroducing resources into production.
Why is tracking important in reverse logistics?
Tracking ensures visibility and transparency throughout the return process. It helps identify bottlenecks, improves efficiency, and builds trust with customers by offering real-time updates on the status of their returns.
Can small businesses adopt reverse logistics?
Yes, small businesses can implement reverse logistics by focusing on simple yet effective practices like clear return policies, basic repair or refurbishment programs, and partnering with local recyclers or logistics providers.
What role do freight forwarders play in reverse logistics?
Freight forwarders specialize in managing the transportation of returned goods. They optimize logistics routes, reduce costs, and ensure timely handling of large-scale returns, making them essential partners in a reverse logistics strategy.