Ocean Freight: A Comprehensive Guide to Global Shipping
Shipping goods across the world requires choosing the right mode of transport. Ocean freight is a reliable and cost-effective option for businesses with large shipment volumes. Here’s a practical guide to help you understand the essentials of ocean freight, sea freight, and how to manage ocean freight rates effectively.
What is Ocean Freight?
Ocean freight refers to the transport of goods using ships and vessels. It is the most commonly used method for international trade. Businesses often choose ocean freight for its capacity to carry large quantities of goods at relatively low costs. From heavy machinery to consumer products, sea freight is the go-to choice for bulk shipments.
Sea freight can handle almost anything. Containers are loaded onto ships, which then travel across the oceans to deliver goods to various parts of the world. Though slower than air freight, ocean shipping is preferred due to its affordability and efficiency for bulk transport.
Types of Ocean Freight Services
When it comes to sea freight, there are several shipping options available. Understanding these options helps businesses choose the best one for their needs.
- Full Container Load (FCL): FCL is the most common choice for businesses that need to ship large quantities. The entire container is dedicated to a single shipper’s goods, reducing the risk of damage.
- Less Than Container Load (LCL): If you don’t have enough goods to fill an entire container, LCL is the right option. Your goods share container space with other shipments, reducing costs.
- Roll-On/Roll-Off (RoRo): RoRo shipping is ideal for vehicles or machinery that can be driven onto the ship. It’s a great option for companies needing to ship large, wheeled cargo like cars and trucks.
- Break Bulk: This service is for cargo that cannot be containerized. Items are loaded individually onto the ship. It’s often used for large construction materials and heavy machinery.
- Refrigerated Shipping (Reefer): When your goods need to be kept at a specific temperature, reefer containers are the solution. This service is commonly used for perishable goods such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Understanding these services is vital for determining efficient ocean shipping solutions that meet your specific needs.
Advantages of Ocean Freight Shipping
Ocean freight offers several key benefits for businesses that rely on shipping goods internationally.
- Cost-Effectiveness: sea freight is significantly cheaper than air freight, especially when shipping large volumes. This makes it the preferred option for businesses looking to reduce shipping costs.
- High Cargo Capacity: Ships can carry massive quantities of goods at once. Whether you need to ship raw materials, finished products, or machinery, sea freight can handle it all.
- Environmentally Friendly: Compared to air freight, sea freight is more eco-friendly. It produces fewer emissions per ton of goods shipped, making it the better choice for companies looking to minimize their carbon footprint.
- Reliable for Large Shipments: For businesses with high shipment volumes, sea freight provides a dependable, cost-effective method. It’s the most scalable option available.
Common Challenges in Sea Freight
Like any shipping method, sea freight does come with its own set of challenges. Understanding these helps businesses prepare and plan better.
- Longer Transit Times: sea freight can take weeks depending on the route. While it’s cheaper, it’s not ideal for businesses needing quick deliveries. Planning ahead is key to managing this challenge.
- Port Congestion: Busy ports can cause delays in loading and unloading. This can affect delivery schedules. However, efficient ocean shipping solutions and good logistics management can mitigate this issue.
- Risk of Damage or Theft: Ocean freight often involves multiple handling processes. Goods can be damaged or stolen if not properly secured. Choosing a reliable freight forwarder and insurance is essential.
- Global Events and Shipping Rates: Natural disasters, political instability, and economic disruptions can lead to unexpected delays and rising ocean freight rates. For instance, trade tensions can disrupt major shipping routes, increasing shipping costs and transit times.
Ocean Freight Rates: Understanding the Costs
Ocean freight rates can vary significantly based on a range of factors. It’s crucial for businesses to understand how these rates are calculated to manage their shipping budgets effectively.
- Base Rates: The base rate is the fundamental cost of shipping goods from one port to another. It typically depends on the shipment’s weight and the distance traveled.
- Surcharges and Additional Fees: These may include fuel surcharges, terminal handling charges, or security fees. Businesses need to be aware of these extra costs when planning their budgets.
- Seasonal Fluctuations: Sea freight rates can increase during peak seasons, such as holidays or festivals. This is often due to higher demand and limited space on vessels.
- How Rates Compare to Air Freight: While ocean freight is far cheaper than air freight, ocean freight rates can still vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. Businesses must decide between the two based on their urgency and budget.
Ocean Freight Rate Calculator
Understanding and estimating sea freight rates is crucial for businesses looking to manage shipping costs effectively. One useful tool for this is GoComet’s Ocean Freight Rate Index, which helps businesses quickly estimate ocean freight rates based on real-time data.
The GoComet Ocean Freight Rate Index allows you to compare rates across multiple carriers, routes, and shipping conditions. This feature helps you make informed decisions by providing accurate, up-to-date pricing based on your shipment’s specific needs. Whether you’re shipping full containers or less-than-container loads, this tool ensures you’re getting the best rate possible.
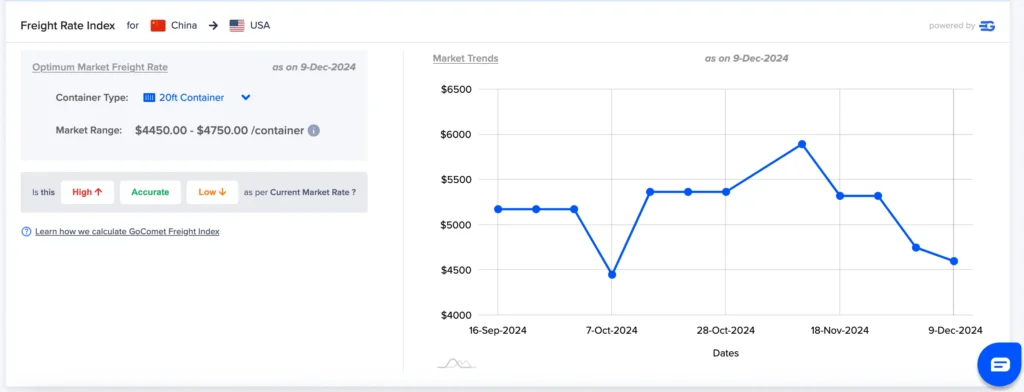
By using GoComet’s Ocean Freight Rate Index, businesses can streamline their budgeting process and optimize shipping costs without the guesswork.
How Ocean Freight Works
Ocean freight involves several key stages from booking to delivery. Understanding the process is essential for ensuring a smooth experience.
- Pre-Carriage: This is the phase before goods are loaded onto the ship. It includes transport from the warehouse to the port and the necessary documentation.
- Main Carriage: The main carriage refers to the time the goods spend on the ship as it travels across the ocean. This phase can take several weeks, depending on the destination.
- On-Carriage: Once the ship reaches its destination port, the goods need to be transported to the final destination. This may involve customs clearance and final delivery by truck or rail.
Managing each stage carefully ensures efficient ocean shipping, which reduces costs and ensures goods reach their destination safely and on time.
Ocean Freight Terminology Simplified
In the world of ocean freight, understanding key terms is crucial. These terms help you communicate more effectively with freight forwarders and shipping companies.
- Freight Forwarders: These are third-party companies that help manage the logistics of shipping goods. They handle booking shipments, documentation, and route planning.
- Incoterms: Incoterms define the responsibilities of the buyer and seller in international trade. Understanding these terms helps avoid confusion about who covers costs and risks at each stage of shipping.
- Container Types: There are several types of containers used in ocean freight, including dry containers, reefer containers, and open-top containers. The right container depends on the type of goods being shipped.
Learning these terms helps businesses streamline their shipping processes and avoid potential misunderstandings with logistics partners.
Ocean Freight vs. Air Freight
Choosing between ocean freight and air freight depends on the nature of your goods and how quickly you need them. Here’s a breakdown:
| Factor | Ocean Freight | Air Freight |
| Cost Comparison | Cheaper, especially for large shipments | More expensive, but suitable for smaller, urgent shipments |
| Delivery Speed | Slower, can take weeks depending on the route | Faster, usually takes days to a week |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, more sustainable | Higher carbon footprint, less sustainable |
| Risk and Reliability | More prone to delays (e.g., weather, port congestion) | More reliable with fewer delays |
Tips for Optimizing Your Ocean Freight Shipping
Optimizing ocean freight is essential for reducing costs and improving efficiency. Here are practical strategies to streamline your ocean shipping process:
- Plan Shipments Early: The longer transit times of sea freight give you more time to plan. Book shipments well in advance to avoid last-minute surcharges and ensure space availability, especially during peak seasons.
- Leverage Relationships with Carriers: Cultivate long-term relationships with trusted carriers and freight forwarders. Strong partnerships can lead to better service, priority handling, and more favorable rates.
- Utilize Freight Management Software: Invest in Ocean Freight Management tools that offer real-time tracking, rate comparison, and route optimization. This technology helps you make data-driven decisions, manage delays, and find the most cost-effective shipping options.
- Consolidate Shipments with LCL: If your shipment doesn’t fill an entire container, Less Than Container Load (LCL) shipping can save money. By sharing container space, you reduce costs while still ensuring your goods reach their destination on time.
By following these strategies, businesses can manage their sea freight efficiently, reduce unnecessary costs, and improve their overall shipping operations.
Conclusion
Choosing the right ocean freight service can save your business time and money. Understanding the types of services available and how ocean freight rates are calculated allows you to make more informed decisions. Whether you’re shipping large quantities or delicate items, there’s a solution tailored to your needs.
By planning ahead, selecting the right partners, and using the right tools, you can navigate the complexities of sea freight and make your shipping process as smooth and cost-effective as possible.
FAQs
How long does ocean freight take?
Transit times vary, typically ranging from 1 to 6 weeks, depending on the origin, destination, and shipping route. Longer routes, especially intercontinental shipments, may take up to 40 days or more.
What products can be shipped by sea?
It can accommodate a wide range of products, from bulk goods like raw materials and industrial equipment to consumer goods, electronics, and perishables (with refrigerated containers). Essentially, if it fits in a container, it can be shipped by sea.
How are ocean freight rates calculated?
Rates depend on the weight of the goods, the type of container, the route, and any surcharges applied.
What are the limitations of ocean freight?
The main limitation is its slower transit times compared to air freight. It’s also less ideal for time-sensitive shipments. Additionally, it can be affected by weather conditions, port congestion, and labor strikes, which may cause delays.
How can I reduce ocean freight costs?
To lower ocean freight costs, consider consolidating shipments (LCL), negotiating long-term contracts with carriers, using freight management software for better route planning, and taking advantage of off-peak shipping periods when rates are lower.
What is the difference between FCL and LCL?
FCL (Full Container Load) is when you rent a whole container for your shipment, offering more control over your goods and usually better rates for large shipments. LCL (Less than Container Load) means sharing container space with other shipments, ideal for smaller loads but often comes with higher costs per unit.
Is ocean freight reliable for large shipments?
Yes, it is very reliable for large shipments, especially when working with experienced freight forwarders. However, factors like port congestion, customs delays, and seasonal demand can occasionally cause disruptions.